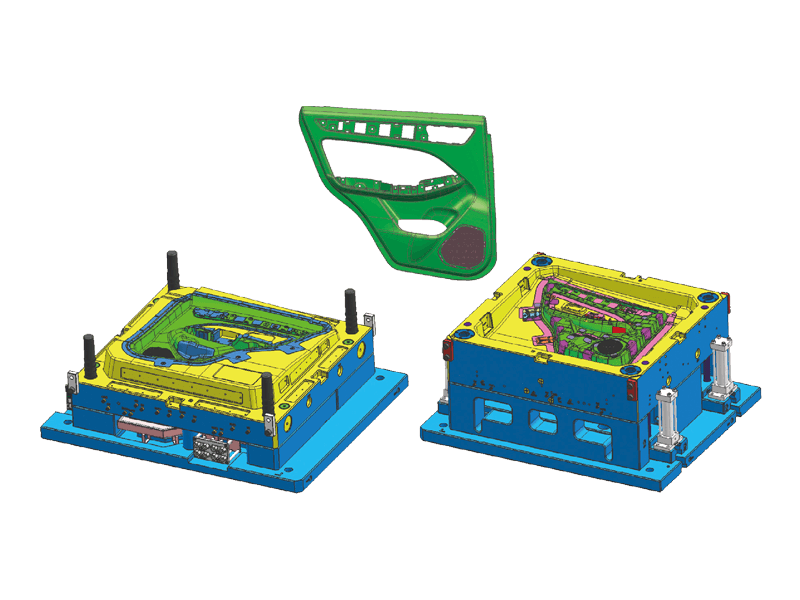
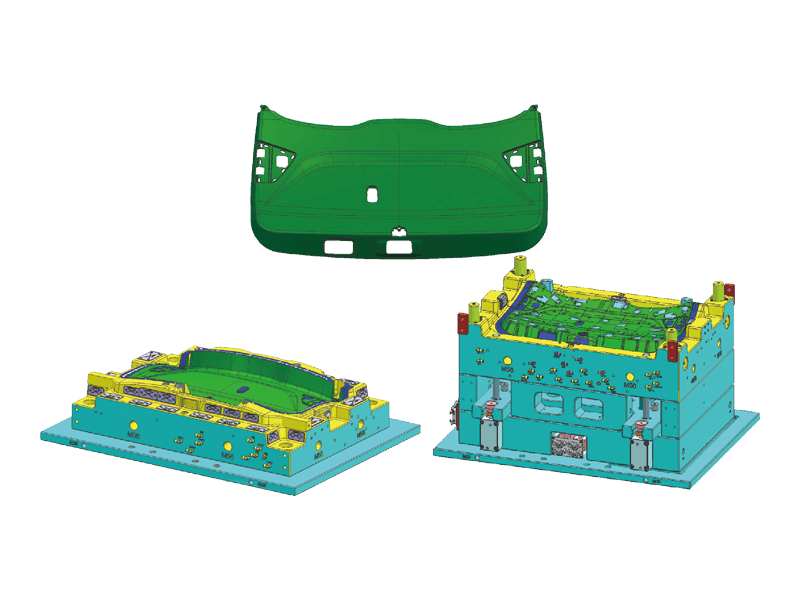
In the automotive industry, the dashboard, or instrument panel, is a critical component that blends functionality with aesthetics. It serves as the control center for drivers, housing essential instruments and features that ensure a safe and enjoyable driving experience. Behind the sleek and polished exterior of these dashboards lies a complex manufacturing process, primarily involving plastic injection molding. This article explores the significance of plastic injection instrument panel molds, examining their design, benefits, applications, and the future of automotive interiors.
Understanding Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create specific shapes and designs. This method is particularly well-suited for producing large volumes of uniform parts, making it ideal for the automotive industry where consistency and quality are paramount.
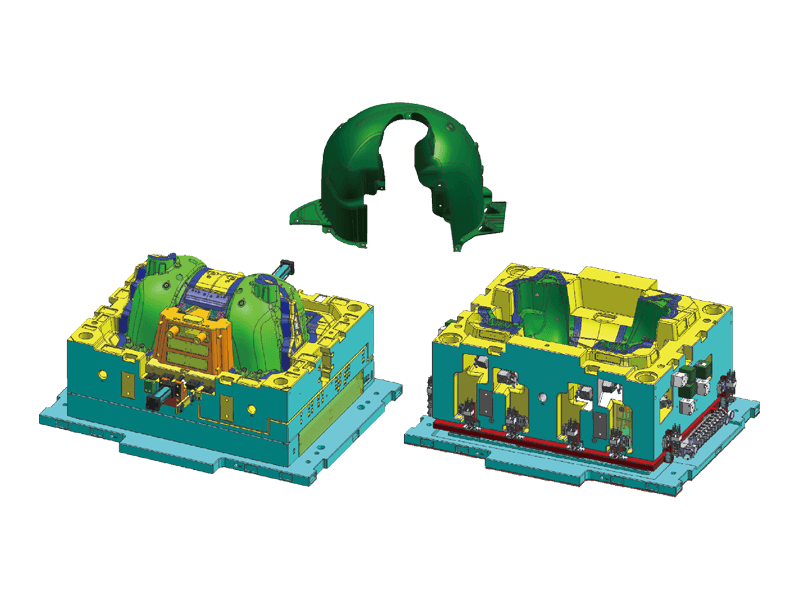
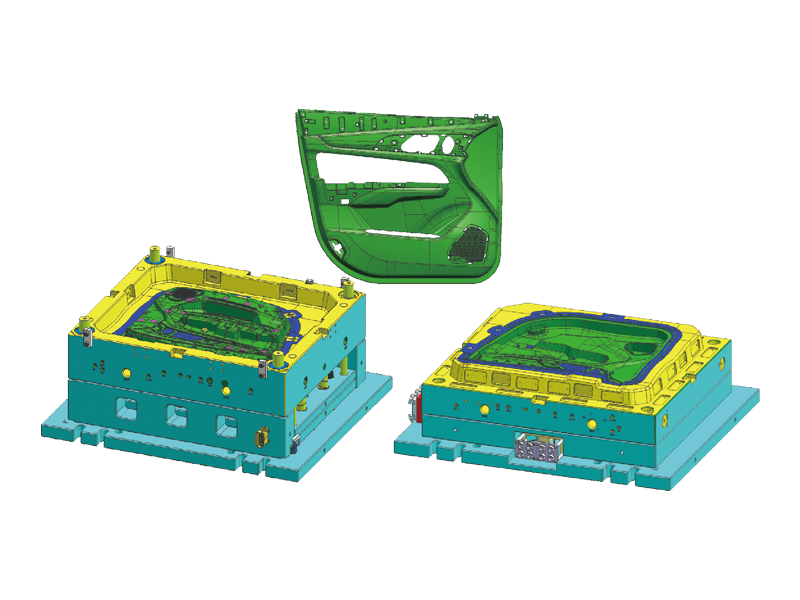
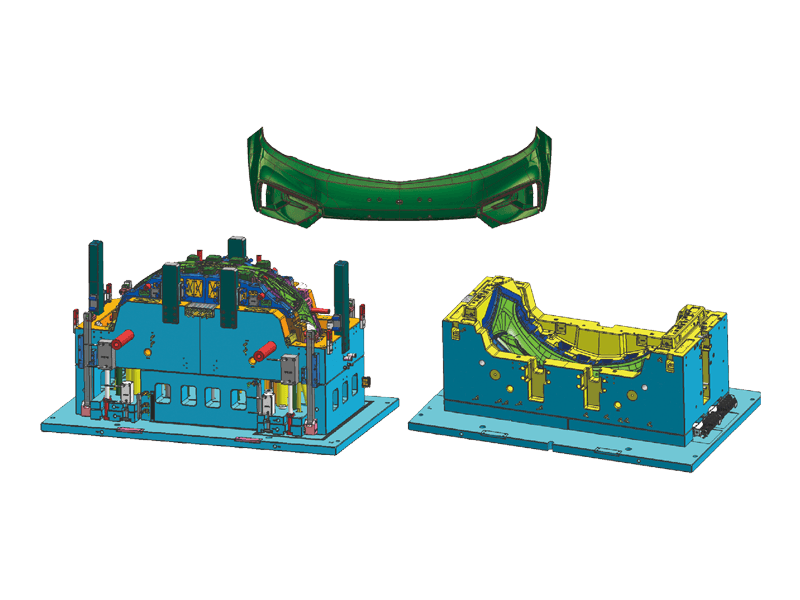
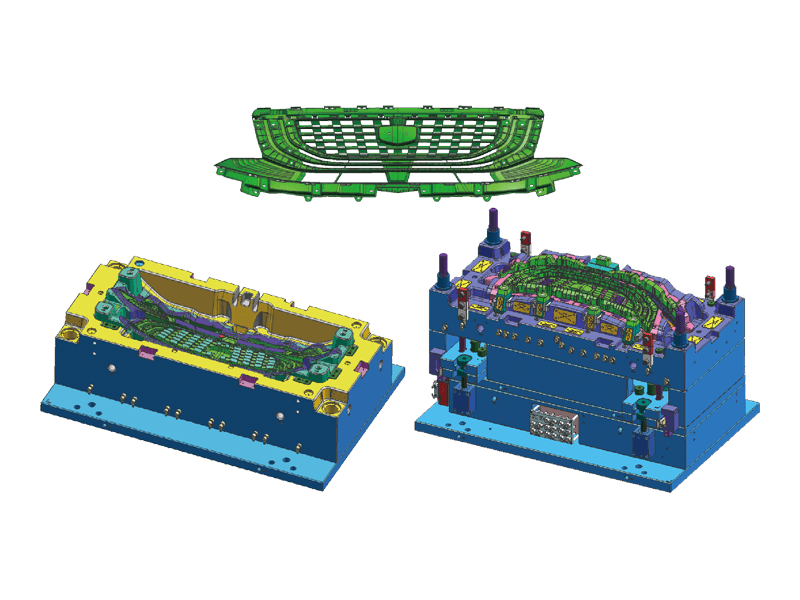
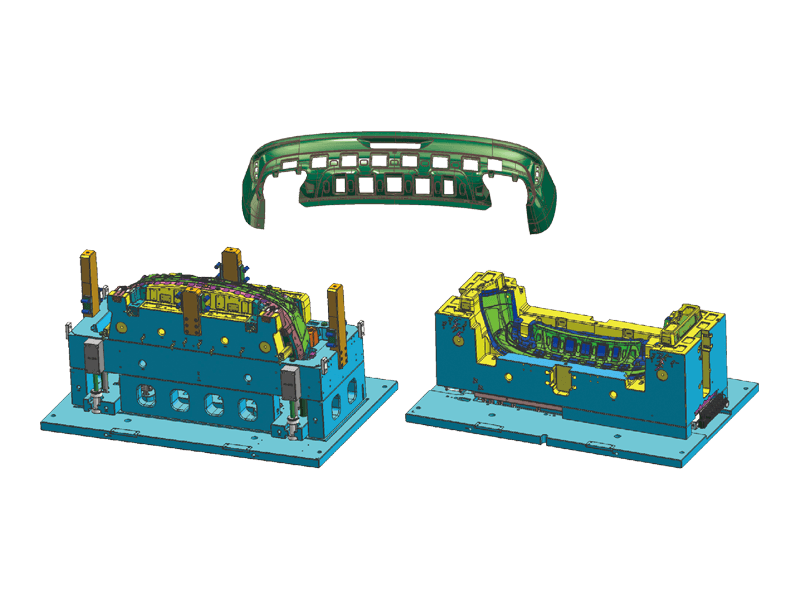
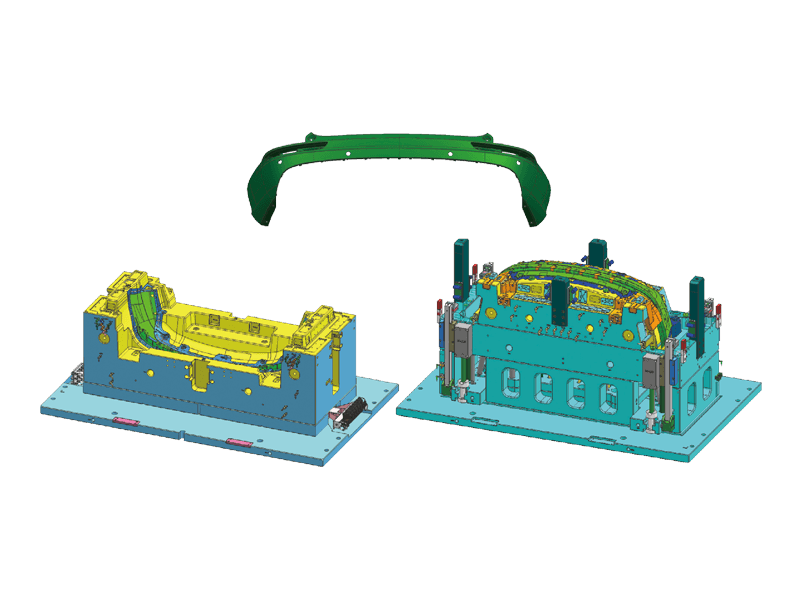
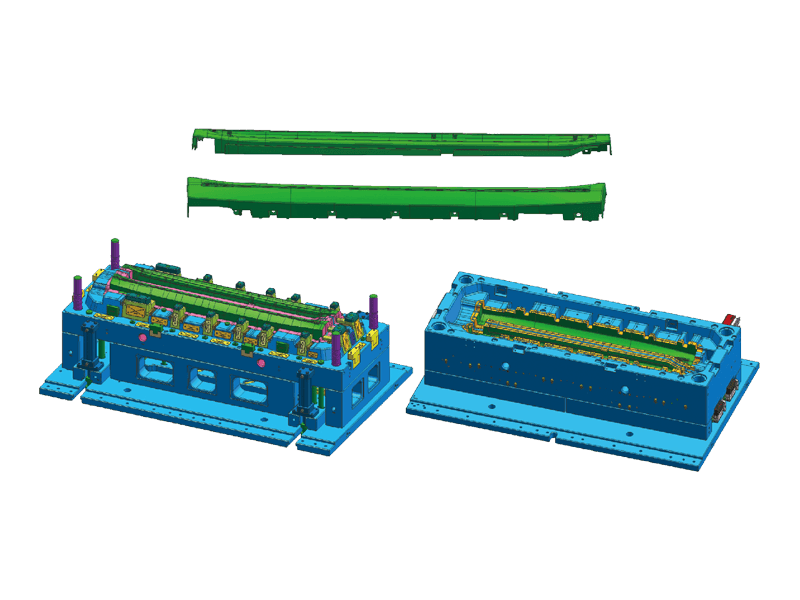
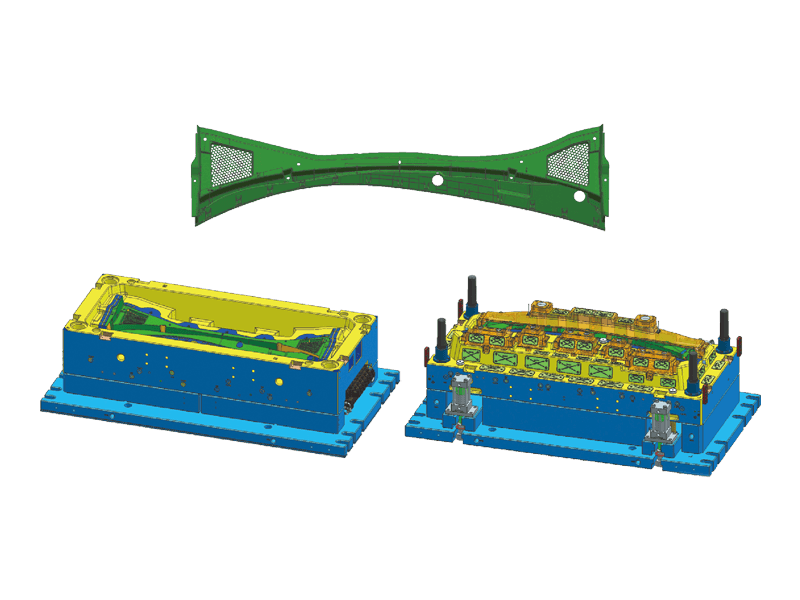
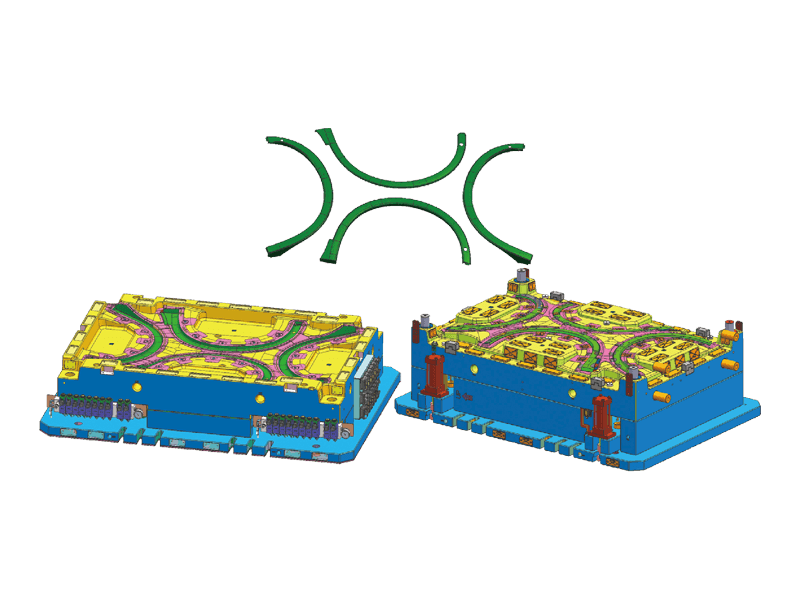
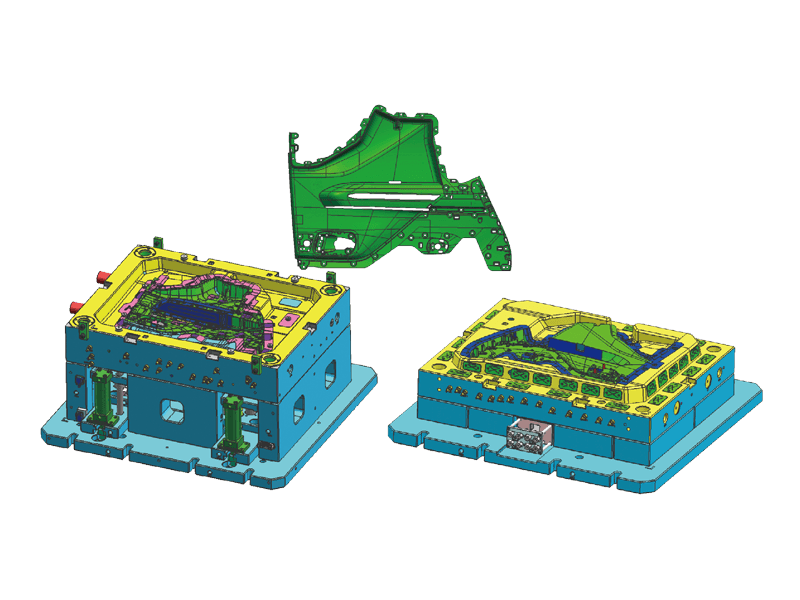
Instrument panel molds are designed to create the intricate shapes and features found in modern dashboards. The process begins with the design of the mold itself, which must accommodate the precise dimensions and specifications of the final product. Designers use advanced software tools to simulate the injection process, ensuring flow and cooling patterns to minimize defects.
The Importance of Instrument Panel Molds
Precision Engineering: Instrument panels must fit perfectly within the vehicle's interior, aligning seamlessly with other components. Molds are engineered to the precision standards to achieve this fit. This level of accuracy is essential for both aesthetic appeal and functional performance.
Complex Features: Modern dashboards often incorporate a variety of features, including digital displays, climate controls, and infotainment systems. Injection molds are designed to accommodate these complexities, allowing for smooth integration of multiple components within a single dashboard.
Material Versatility: The choice of materials used in the injection molding process is crucial. Instrument panels are typically made from high-quality plastics that offer durability, resistance to UV light, and a pleasing appearance. Common materials include ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and PC (Polycarbonate), which provide a balance of strength and flexibility.
Surface Finishing Options: The visual aspect of instrument panels is vital, as they are one of the visible components of a vehicle's interior. Molds can be designed to accommodate various surface finishes, including matte, gloss, and textured surfaces. This versatility allows manufacturers to meet different design specifications and consumer preferences.
Benefits of Using Injection Molds for Instrument Panels
Cost Efficiency: While the initial investment in mold creation can be significant, injection molding offers substantial cost savings for high-volume production. The ability to produce large quantities of parts with minimal waste leads to lower overall costs.
Speed and Efficiency: The injection molding process is rapid, with cycle times often measured in seconds. This speed allows manufacturers to keep up with high demand in the automotive industry, reducing times and improving responsiveness to market changes.
Consistency and Quality Control: Injection molding ensures that each part produced is consistent in quality and appearance. Automated processes and strict quality control measures minimize variations, ensuring that every instrument panel meets the required specifications.
Design Flexibility: The design capabilities of injection molding are extensive, allowing manufacturers to create intricate shapes and features that enhance the functionality and aesthetics of instrument panels. This flexibility supports the trend toward more innovative and personalized vehicle interiors.
Applications of Plastic Injection Molds in Instrument Panels
Plastic injection molds for instrument panels are used to produce a wide range of components, including:
Main Dashboard Assemblies: The core structure that houses various controls and displays.
Gauge Clusters: Molds create the housing for speedometers, tachometers, and other essential gauges.
Control Panels: Customized molds enable the production of panels that integrate climate control, audio systems, and navigation features.
Storage Compartments: Injection molds are also used to create storage compartments and trays within the dashboard, enhancing functionality and organization.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体